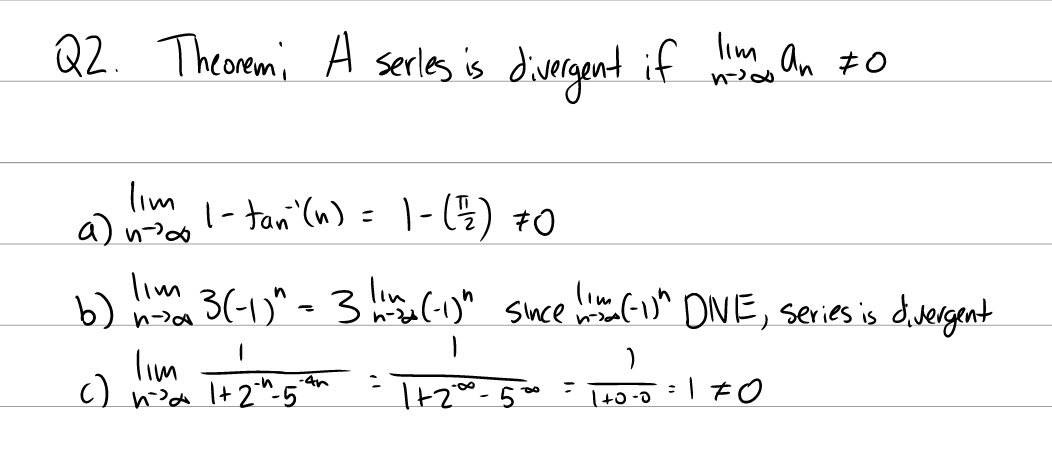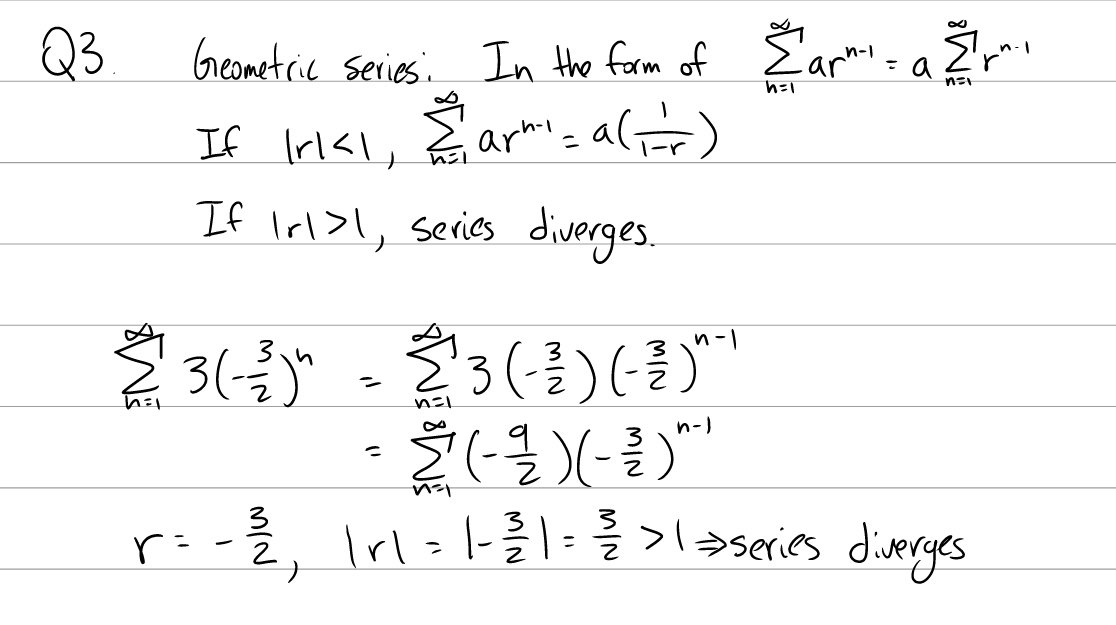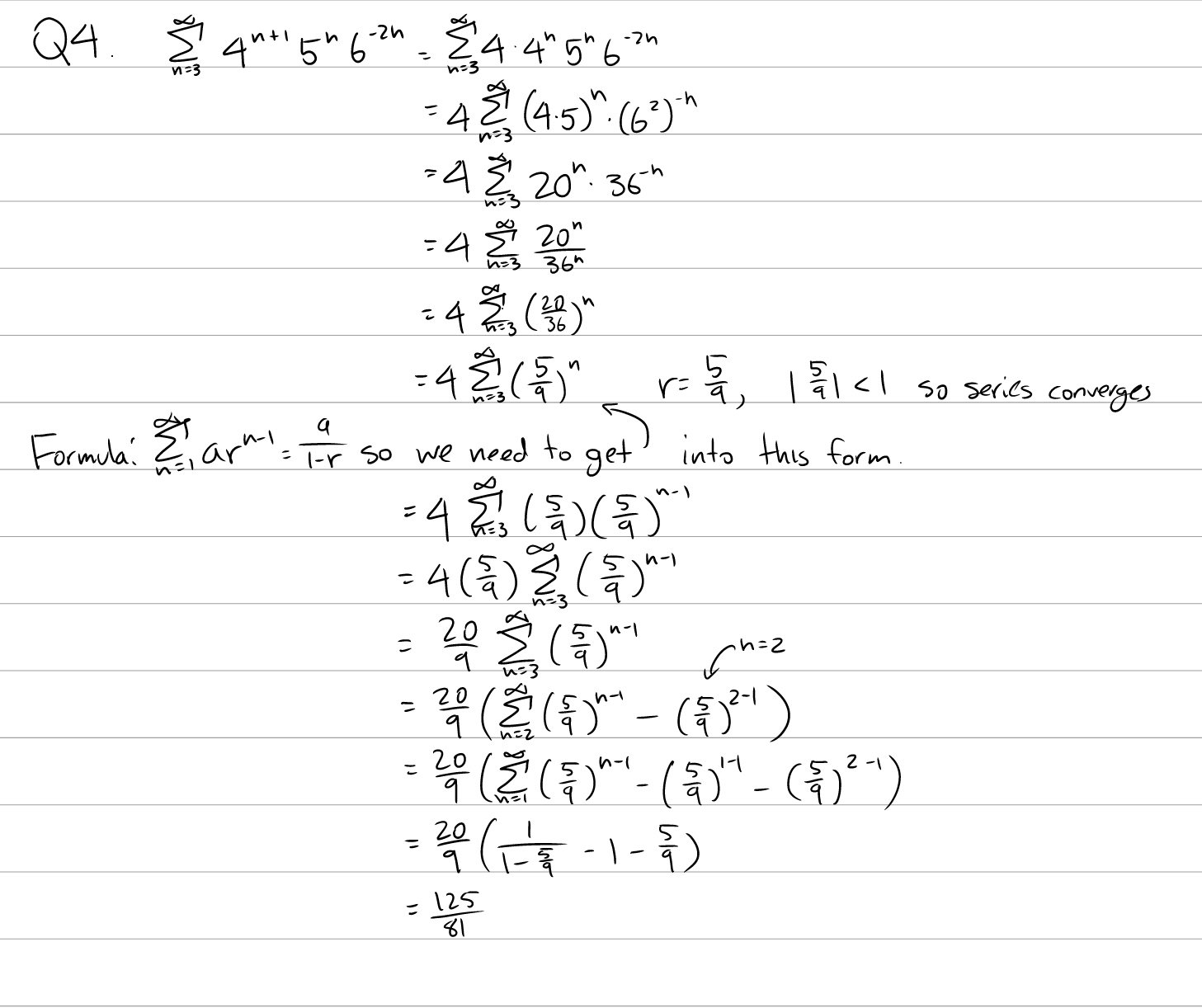Tutorial Week 11
Series Definitions
A series is a sum written in the form \(\sum_{k=1}^\infty a_k\).
A series converges if \(\sum_{k=1}^\infty a_k = L\) for some constant L.
If no such \(L\) exists, then the series diverges.
The divergence test states that if \(\lim_{k \to \infty} a_k \ne 0\), then a series diverges.
Geometric Series
A geometric series is a series in the form of \(\sum_{k=0}^\infty ar^k\).
If \(|r| \lt 1\), then the series converges to \(\frac{a}{1-r}\).
If \(|r| \ge 1\), the series diverges.
Q1: Does \(\sum_1^\infty 1 - \arctan(n)\) converge? If so, find its sum.
Q2: Does \(\sum_{n=1}^\infty 3(-\frac{3}{2})^n\) converge? If so, find its sum.
Q3: Does \(\sum_{n=3}^\infty 4^{n+1}5^n6^{-2n}\) converge? If so, find its sum.
Comparison Test
The comparison test states:
Given series \(\sum a_n\) and \(\sum b_n\), where \(a_n \ge 0\) and \(b_n \ge 0\),
If \(\sum a_n\) converges and \(b_n \le a_n\), then \(\sum b_n\) converges.
If \(\sum a_n\) diverges and \(a_n \le b_n\), then \(\sum b_n\) diverges.
Q4: Use the comparison test to show whether \(\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{3n + 5}{2^n + 5^n - 1}\) converges.
Alternating Series Test
The alternating series test states:
Given an alternating series in the form of \(\sum (-1)^n b_n\) where \(b_n \gt 0\), if \(b_n\) forms a decreasing sequence (\(b_{n+1} \le b_n\)) and \(\lim_{n \to \infty} b_n = 0\), then \(\sum (-1)^n b_n\) converges.